IEEE Access
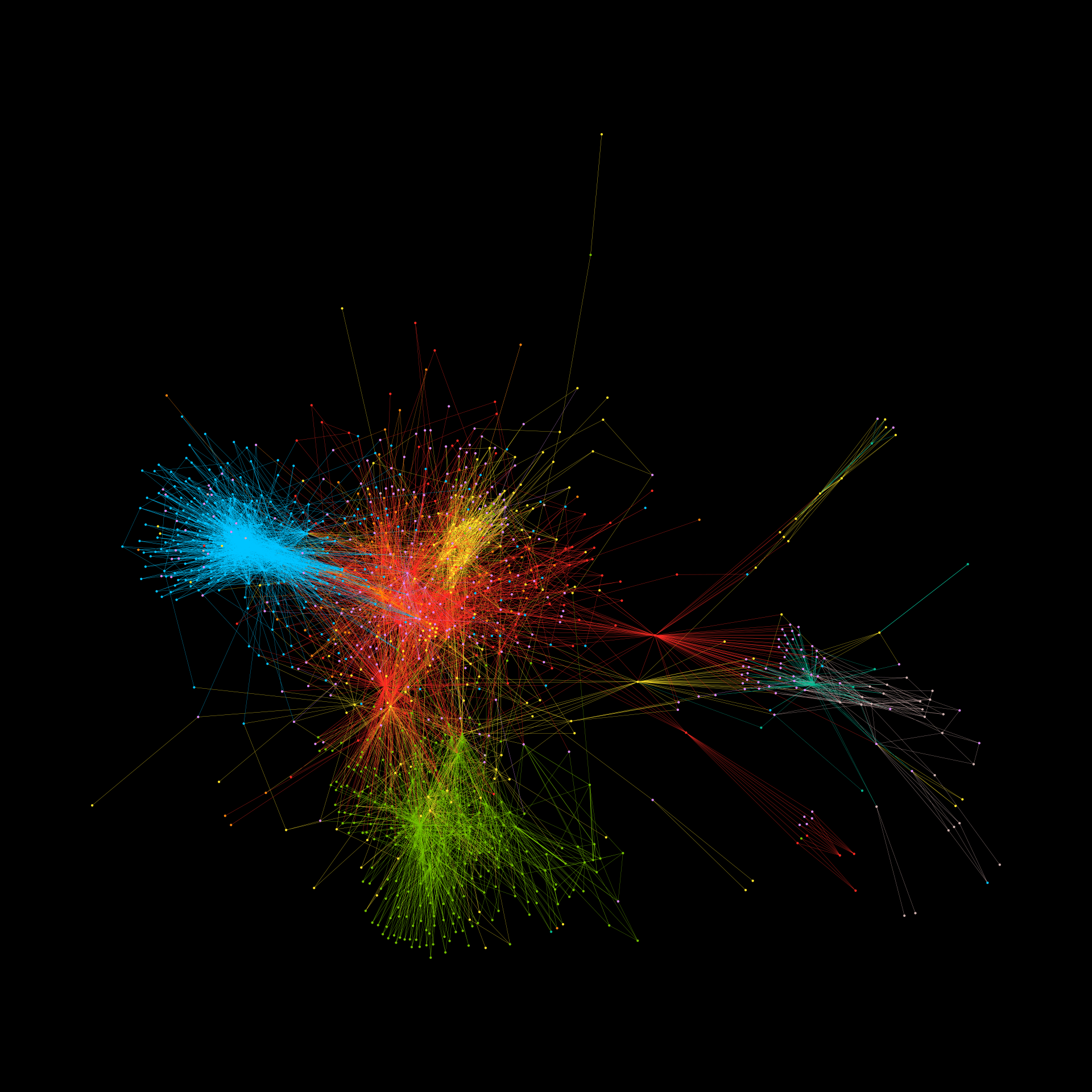
The prevalence of dangerous misinformation and extreme views online has intensified since the onset of Israel-Hamas war on 7 October 2023. Social media platforms have long grappled with the challenge of providing effective mitigation schemes that can scale to the 5 billion-strong online population. Here, we introduce a novel solution grounded in online network engineering and demonstrate its potential through small pilot studies. We begin by outlining the characteristics of the online social network infrastructure that have rendered previous approaches to mitigating extremes ineffective. We then present our new online engineering scheme and explain how it circumvents these issues. The efficacy of this scheme is demonstrated through a pilot empirical study, which reveals that automatically assembling groups of users online with diverse opinions, guided by a map of the online social media infrastructure, and facilitating their anonymous interactions, can lead to a softening of extreme views. We then employ computer simulations to explore the potential for implementing this scheme online at scale and in an automated manner, without necessitating the contentious removal of specific communities, imposing censorship, relying on preventative messaging, or requiring consensus within the online groups. These pilot studies provide preliminary insights into the effectiveness and feasibility of this approach in online social media settings.